If your guitar is not set-up properly, a few things can
happen.
One: Your guitar may
be perfectly in tune at the nut (i.e. the 0th fret), but it will get
progressively more out of tune the further up-the fretboard you play (i.e. the
open E on your sixth string will be in tune, but the E at the 12th
fret on your sixth string will be sharp or flat.). Adjusting your guitar so that it is in tune
along the entire fretboard is known as adjusting the intonation.
Two: The further up
the fretboard you move, the more your fingers feel like they are walking in
deep snow. This is because the neck of
your guitar is not adjusted properly and is slightly concave. Adjusting your guitar so that the fretboard
is neither concave nor convex is known as adjusting the truss rod. The other possibility is that the saddle height at the bridge needs adjusting.
Three: When playing
fretted notes at the low end of the fretboard, the string will sound the note,
but also makes a buzzing sound. This is
because the neck of your guitar is not adjusted properly and is slightly
convex. Adjusting your guitar so that
the fretboard is neither concave nor convex is known as adjusting the truss
rod. The other possibility is that the saddle height at the bridge needs adjusting.
So a guitar that is not set-up properly will not sound good
and will be difficult to play, which will make for a frustrating experience for
a beginner. Thus, the first thing you
should do after you buy your first guitar is get is set-up. This will set you back $50 to $75. This may sound a bit steep if you only spent
$200 on your guitar, but it's worth it for the frustration it will save you.
ADJUSTING THE
INTONATION
Why is it that your guitar can be in tune at the nut and out
of tune at the 12th fret? A
little bit of physics comes into play here.
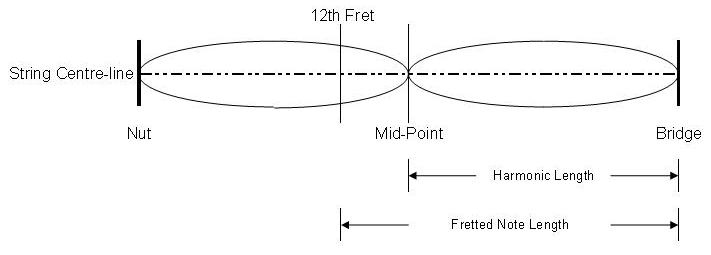
When you pick an open string, the string vibrates in one continuous arc
that starts at the nut and ends at the bridge.
The frequency of the low E string played open is ~ 82 Hz
If the string vibrates twice as fast, there will be two arcs,
the first between the nut and the string’s mid-point, and the second between
the mid-point and the bridge (see footnote).
At the mid-point of the string, there will be a node (i.e. a point where
the string is not moving). The note you
now hear is the first octave above the sound of the open string.
Vibrating twice as fast, the frequency produced by your low
E string will now be ~ 164 Hz (i.e. it doubles). So when you play the note at the 12th
fret of your low E string, what you should hear is the E one octave higher than
the open string (because the 12th fret is meant to be the octave).
But what if the mid-point of the string is not centered over
the twelfth fret? Then the note you hear
when you play at the twelfth fret of your low E string will not be the octave, and instead will either be sharp or
flat. To get that note in-tune, you need
to centre the mid-point of the string over the twelfth fret. This is done by adjusting the length of the
string at the bridge.
Daddy, What’s a Harmonic?
Now, how do you know whether to lengthen or shorten the
string? To answer this question, you
first need to learn how to play a harmonic.
Place your finger so that it is lightly touching the string at the 12th
fret (do not press down and fret the note!).
Pick the string. What you hear
will be an octave higher than the open string.
When you pick the string, it normally vibrates in one
continuous arc. Placing your finger
lightly on the string at the 12th fret creates a node and forces the
string to vibrate with two arcs. The
notes resulting from forcing nodes like this are called harmonics. There are several of them on your
fretboard. Now that you know what a
harmonic is, let’s go back to figuring out if our string is too long or too
short.
Don’t ask for Shorter Strings at the Guitar Store!
If the true mid-point of the string is below the twelfth
fret, then the harmonic will have a longer arc than the fretted note at the 12th
fret and thus will have a lower pitch.
So if the harmonic is a lower pitch than the fretted note, you need to
lengthen the string. This will move the mid-point towards the bridge (and the 12th fret).
If the true mid-point of the string is above the twelfth
fret, then the harmonic will have a shorter arc than the fretted note at the 12th
fret and thus will have a higher pitch.
So if the harmonic is a higher pitch than the fretted note, you need to
shorten the string. This will move the mid-point towards the nut (and the 12th fret).
To test this, you will need an electronic tuner (see Confession #2 - Tune Your Guitar!).
Methods of adjusting the string length will vary from guitar
to guitar as different manufacturers use different kinds of bridges. Consult your manufacturer’s website for
guidance for your particular bridge. In some cases it is not
possible to adjust the intonation due to the bridge design. Most acoustics (if not all) are not
adjustable.
 |
| Fender Telecaster Bridge Intonation is adjustable for each string. Note the hex-key screws for adjusting saddle height. |
 |
| Paul Reed Smith SE Custom Bridge Intonation is not individually adjustable for each string, but the bridge position relative to the two set screws can be adjusted. |
 |
| Yamaha APX 500 Bridge Intonation is not adjustable. |
When you're done, the mid-point of the string will be centered over the 12th fret, like this:
This next tip is in big bold letters because its very important.
Because you've changed the length of the string, the open string will need to be re-tuned when you've finished adjusting the string's intonation!
You're done. Enjoy your properly intonated and freshly tuned guitar!
Footnote: You can
see this visually if you take a long piece of rope and anchor one end to a
stationary object, like a tree. Hold the
other end in your hand and with the rope taught, shake your hand up and down
until you see the aforementioned continuous arc. It’s called a standing wave. Now move your hand up and down faster and
faster until you see the pair of arcs, with a stationary node in the middle.
ADJUSTING THE TRUSS
ROD AND SADDLE HEIGHT
Inside the neck of your guitar is an adjustable rod, called
the truss rod. This is used to adjust
how concave or convex the neck of the guitar is.
If the neck is concave, the strings will sit high off the
fretboard and you’ll find it difficult to move from string to string. Your fingers will feel like they are walking
in deep snow.
If the neck is convex, the strings will sit low to the
fretboard and may buzz against higher frets (e.g. you playing the C at the 3rd
fret of the 5th string and the string buzzes against the 4th
fret when you play the note.
Of course, if the saddle height is not set properly, this can also cause the same problems.
Adjusting the truss rod is something best left to an experienced
guitar tech. If you adjust it too much
one way or the other, you can damage the neck.
Knowing whether the truss rod needs adjusting, or the saddle height needs adjusting, or both, is again something that is best left to an experienced guitar tech. If you don't know what you're doing, you could just end up making things worse.
Knowing whether the truss rod needs adjusting, or the saddle height needs adjusting, or both, is again something that is best left to an experienced guitar tech. If you don't know what you're doing, you could just end up making things worse.




GREAT INFO! THANK YOU VERY MUCH! NICE WORK HERE! =D
ReplyDelete